Knowledge Center
NTC sensor – Information
Introduction #
A thermistor is an electronic component that changes resistance to temperature – so-called Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTD).
A Thermistor is a resistor that changes its resistance with temperature. In temperature measurements we typically use a NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient) Thermistor. For NTC thermistors we have that the resistance gets lower when the temperature gets higher.
We will use a 10K NTC Thermistor in this tutorial. A 10K Thermistor has a resistant R = 10K @ 25°C.
Steinhart-Hart equation
There is a non-linear relationship between resistance and excitement. To find the temperature we can use the Steinhart-Hart equation:
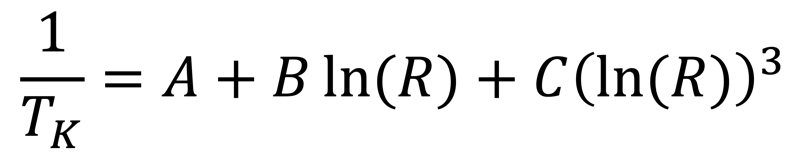
where A = 0.001129148, B = 0.000234125 and C = 8.76741E−08.
Tk is the Temperature in degrees Kelvin and R is the resistance.
Voltage Divider #
When using NTC on microcontrollers or other devices we are only able to read a voltage level using the built-in Analog to Digital Converter (ADC). This means we need to create and use a so-called Voltage Divider in order to be able to read the voltage level and then we can calculate the Resistance R that flows through the Thermistor.
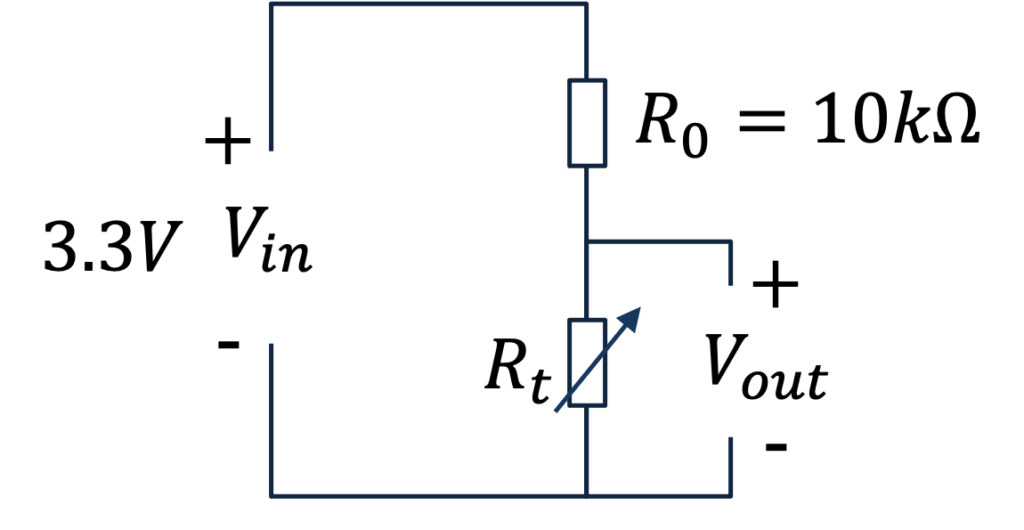
Below you see a Voltage Divider:
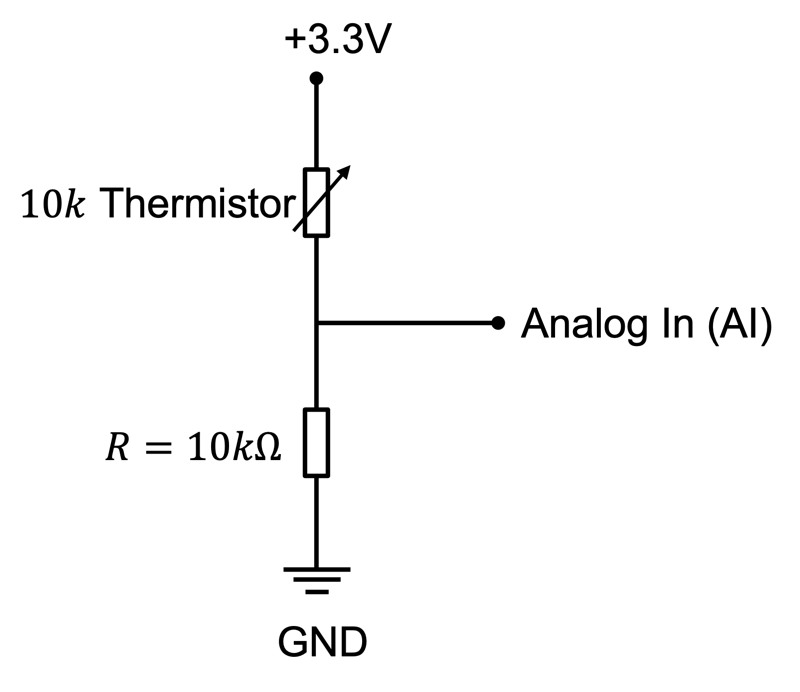
In addition to the 10K Thermistor where the resistance changes with the temperature we use a 10K Ohm Resistor.
Below you see a general Voltage Divider:
The general Voltage Divider Equation is as follows:
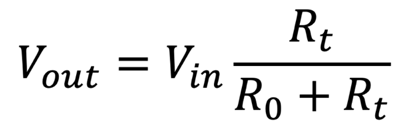
Vout is the voltage level we read using the ADC on the Raspberry Pi Pico.
We reformlate in order to find the Resistance (Rt) flowing through the Thermistor:
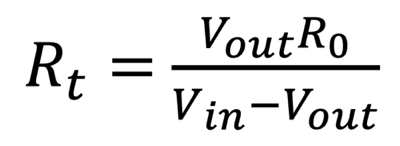
The value of the resistor (Ro) should be roughly equal to the resistance of your thermistor. The accuracy will be poorer if the value of the known resistor (Ro) is much smaller or larger than the resistance of the unknown resistor Rt (Thermistor).
We need to do the following steps to calculate the temperature
- We measure Vout using the ADC on Raspberry Pi Pico
- We calculate Rt using the Voltagee Divider Equation
- Then we use Steinhart-Hart equation for finding the Temperature
- Finally we convert from degrees Kelvin to Celsius

Products #
Source #
https://halvorsen.blog/documents/technology/iot/pico/pico_thermisor.php